
In working cardiomyocytes, such as ventricular or atrial myocytes, the resting membrane potential during diastole, or phase 4 of the cardiac action potential, is determined by the baseline ionic and charge gradients that exist across the sarcolemmal membrane. The cardiac action potential is divided into phases, each reflecting the major ionic movements that take place. Regardless of the underlying pathology, the effects on action potential behavior may trigger arrhythmic activity. However, a number of pathologic stressors influence channel activity, including acquired syndromes that are associated with cardiac hypertrophy and failure, as well as an ever-growing number of congenital diseases. Channel function and, by extension, action potential behavior are dynamically tuned in response to normal physiologic factors, especially heart rate. The behavior of these ionic pathways is highly regulated, and permeation of specific ions is influenced by multiple factors, the most prominent of which are changes in membrane potential (i.e., voltage gating), ligand binding, second messengers such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and post-translational modification.

These ions traverse the cell membrane through ion-selective pores formed by assemblies of integral membrane-spanning proteins and accessory proteins. The cardiac action potential, which reflects the integrated behavior of numerous individual ionic currents, is largely dominated by the movement of Na +, Ca 2+, and K + ions.

During each cardiac cycle, ions move back and forth across the cardiomyocyte cell membrane, thereby changing V m. 55-1) is a recording of a cell’s membrane potential, V m, versus time. thank you therefore beacuseknow that cardiac action potential is caused therefore because yes.Lee Goldman MD, in Goldman-Cecil Medicine, 2020 The Cardiac Action Potential You are advised to independently verify the claims in the articles and make your own conclusion.
#Action potential graph free
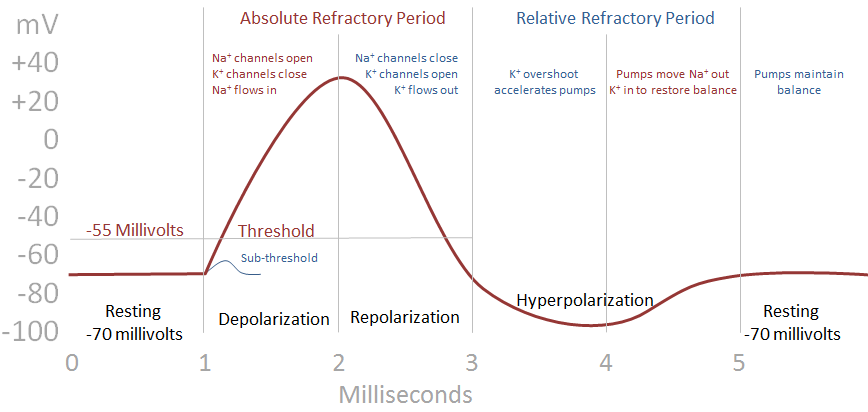
While we tried hard to write quality articles but still, the articles and the information within them is not guaranteed to be free of factual errors or typos and hence may not be correct. The information provided on this website (is only for educational purpose and is Copyrights Protected. Phase 4 is the resting membrane potential. Therefore the high potassium conductance results in large outflow of current which results in the hyperpolarization of the membrane. calcium conductance is decreased in this phase and potassium conductance increases. During this phase, outward and inward currents are equal and thus maintains the plateau phase. It is the plateau of the action potential that is caused by a transient increase in calcium conductance inside the cell. It is caused by an increased outflow of potassium ions out of the cell and decreased inflow of the sodium ion. Phase 1 begins with initial repolarization. At the peak of action potential, the membrane potential approaches the sodium equilibrium potential. this results in depolarization of the membrane. It is caused by a sudden increase in sodium inflow. Phases of Cardiac Action Potential Phase 0 Or inward current that brings positive charge/ions out the cell and causes depolarization of the cell membrane. It is caused by the movement of positive ions out of the cardiac cell. Or inward current that brings positive charge/ions into the cell and causes depolarization of the cell membrane. It is caused by the movement of positive ions into the cardiac cell. because Basic Terminologies Depolarization The RMP (Resting membrane potential) is determined by the conductance to potassium ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
